As solar energy becomes a key solution for residential, commercial, and industrial energy needs, the solar inverter stands out as a vital component in ensuring performance, reliability, and return on investment (ROI).
Whether you’re a B2B buyer, solar installer, homeowner, or procurement manager, this guide will walk you through the essentials of choosing the best inverter in 2025.
Solar inverters do more than convert electricity. They act as the operational hub of the solar system—monitoring, regulating, protecting, and optimizing your power output.
With the surge in solar adoption across households, manufacturing plants, office buildings, retail centers, and utility-scale farms, selecting the right inverter is more important than ever.
What is a Solar Inverter?
A solar inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) generated by photovoltaic (PV) panels into alternating current (AC) used by most electrical equipment and the grid.
For both home and commercial systems, inverters also play key roles in:
- System optimization with MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
- Safety management and auto shutdown
- Remote monitoring and diagnostics
- Battery integration and smart grid control
- Fault detection and real-time reporting
Without a high-performance inverter, even the best solar panels cannot deliver expected energy savings or grid compliance.
How Does a Solar Inverter Work?
When solar panels capture sunlight, they generate DC electricity. The inverter then:
- Converts DC to usable AC power.
- Matches grid voltage and frequency (for grid-tied systems).
- Optimizes power output using MPPT algorithms.
- Communicates performance data via apps or portals.
- In grid-tied systems, the inverter shuts down during grid failure for safety.
- In hybrid systems with batteries, it can continue powering essential loads during outages.
Some advanced models also include arc-fault protection, zero-export functionality, and reactive power control—key features for grid compliance and household safety.
Types of Solar Inverters and Their Applications
When it comes to selecting a solar inverter, understanding the different types—and their best-fit applications—is essential. Each inverter type is engineered with a specific scale, layout, and usage scenario in mind.
Here’s a more intuitive breakdown:
String inverters
String inverters are the most widely used, especially for residential and small to medium commercial systems. They work by connecting a “string” of solar panels to a single inverter.
This centralized approach is affordable and efficient when panels receive uniform sunlight. However, if one panel is shaded or underperforming, the entire string’s output can be affected.
Micro inverters
Micro inverters, in contrast, are mounted individually on each panel.
This allows every panel to operate independently, making them a popular choice for rooftops with partial shading, multiple orientations, or irregular layouts—common in residential setups.
Micro inverters simplify fault detection and enhance flexibility when expanding a system.
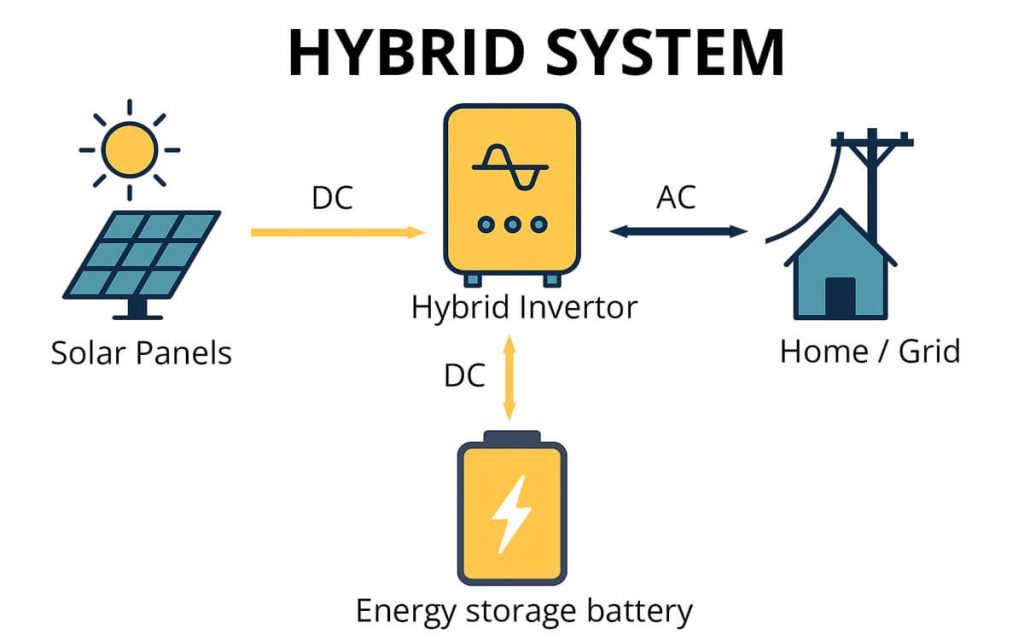
Hybrid inverters
Hybrid inverters are the modern multitaskers of solar energy. They not only convert DC to AC but also manage battery charging and discharging.

Hybrid systems are ideal for users who want grid independence, backup power, or energy cost optimization through load shifting. They’re increasingly adopted in both homes and businesses seeking stability and flexibility.
Central inverters
Central inverters are the powerhouses designed for utility-scale solar projects and large commercial or industrial sites.
These units can handle hundreds of kilowatts or even megawatts of power. They offer cost-efficiency at scale but require dedicated cooling, larger installation areas, and more complex maintenance protocols.
Grid-Tied vs Off-Grid vs Hybrid Inverters
Not all solar systems operate the same way—and neither do the inverters that power them.
Understanding the differences between grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid inverters can help you design a solar solution that fits your energy needs, budget, and level of grid dependence.
Each has distinct advantages and is suitable for specific types of users and installation environments.
| System Type | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Grid-Tied | Feeds power into the utility grid | Homes, offices, commercial buildings |
| Off-Grid Solar Power System | Fully independent with battery storage | Remote cabins, farms, or industrial sites |
| Hybrid | Grid + Battery integration | Homes with energy storage, businesses seeking backup power |
Hybrid systems are increasingly popular among homeowners and industrial zones where grid outages can disrupt operations. They ensure continuity and allow better energy cost control.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Solar Inverter
With so many inverter models, technologies, and configurations on the market, narrowing down the best choice can feel overwhelming. But making the right selection is critical to achieving maximum energy yield, system safety, and long-term reliability. Whether you’re planning a rooftop solar setup for your home or managing a large-scale installation for a commercial building, the following factors will help guide your decision.
Power Rating & Compatibility
The inverter must align with your solar panel array’s total output and the grid requirements in your region. For example, a typical residential system may require a 3–10kW inverter, while large commercial systems often demand 30kW or more. Also consider voltage compatibility—some inverters support 208V, 240V, or 480V configurations depending on the region and application. with your system size, panel configuration, voltage, and local grid standards.
MPPT Inputs
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) inputs help your inverter extract the most energy from each panel string, even when conditions vary. Residential systems with simple roofs may only need one MPPT, but commercial arrays with east-west orientations or shading differences benefit from two or more MPPTs for better performance. better optimization for multi-angle or multi-orientation panel arrays, useful in both homes and commercial setups.
Efficiency
High efficiency means more of your solar power gets converted into usable energy. Inverters with 98%+ conversion efficiency and advanced thermal management help reduce losses—especially important in hot climates or continuous-load commercial use. ≥98% conversion efficiency and ≥99% MPPT efficiency. Higher efficiency translates to lower energy losses and improved ROI.
Safety & Certification
Make sure your inverter complies with safety and grid standards relevant to your country or region. Certifications such as CE, UL1741, or IEC62109 ensure the inverter has passed rigorous testing for electrical protection, grounding, and grid synchronization. These are essential for both residential permits and commercial inspections. and regional standards like CE, UL1741, IEC62109, and VDE-AR-N 4105 to ensure compliance and safety.
Smart Monitoring
Modern inverters come equipped with monitoring tools—via mobile apps, cloud platforms, or integrated dashboards. These allow homeowners to track daily energy savings and let facility managers detect performance drops or failures in real time, avoiding costly downtime. real-time yield data, diagnostics, and fault alerts. This minimizes O&M costs and helps you detect issues early—whether on your rooftop or factory.
Warranty & After-Sales Service
Inverter warranties are more than a number—they reflect the manufacturer’s confidence and support structure. A 5–10 year warranty is typical for home use, while industrial-grade systems often come with 10–15 years. Also check for regional service partners or spare parts availability before purchase. (typically 5–10 years for residential and up to 10–15 years for industrial) and accessible service centers are critical for reliability and peace of mind.
Best Solar Inverter Brands in 2025 (for Home & Commercial Use)
With a growing number of inverter manufacturers entering the market, choosing a trusted brand is a decision that affects everything from daily performance to long-term maintenance costs. A quality brand offers more than just efficiency—it provides reliable customer support, warranty coverage, and local compliance, all of which are crucial for both home users and commercial project developers.
Here’s a look at some of the top inverter brands in 2025, along with their target markets and distinguishing features:
| Brand | Target Market | Strengths | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sungrow | Residential/Commercial | Affordable, global service network | Strong presence in Asia & EU |
| Huawei | Utility/Hybrid | AI-based monitoring, high reliability | Local support may vary |
| SMA | Residential/Industrial | Robust German quality | Premium pricing |
| Growatt | Homes & SMEs | Cost-effective, wide product line | Great for first-time users |
| Fronius | Residential/Commercial | Modular design, long service life | Excellent European support |
Each of these brands has its own strengths. For example, a homeowner might prefer Growatt for its ease of use and affordability, while a commercial EPC firm might favor SMA or Huawei for advanced monitoring and industrial durability. Consider factors like local availability, technical support, and software compatibility when making your final selection.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting for Solar Inverters
Even high-quality inverters are subject to occasional faults, especially when operating under extreme conditions or in aging systems. Recognizing the most frequent issues can help users—whether homeowners or facility managers—act quickly to restore performance and avoid larger system failures. Below are common inverter problems and practical troubleshooting tips:
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No Output | Panel or grid disconnect | Check breakers, fuses, connections |
| Overheating | Poor ventilation | Relocate or improve airflow |
| Ground Fault Errors | Moisture or wire insulation issue | Inspect and replace damaged cables |
| Reduced Efficiency | Shading or mismatched strings | Reconfigure or optimize layout |
Proactive monitoring systems often alert you before failure occurs. Many modern inverters come equipped with mobile or web apps that allow users to identify anomalies early. Regular system checkups and log reviews are especially valuable for commercial setups, but homeowners can benefit equally from these preventive practices. often alert you before failure occurs, enabling preventive maintenance—crucial for homeowners and facility managers alike.
How to Improve Your Solar Inverter Efficiency
Even the best inverters require attention to operate at their full potential. Over time, dust, heat, wiring degradation, and system mismatch can all reduce efficiency—leading to lower energy yield and a slower return on investment. The good news? With just a few maintenance practices and thoughtful design choices, you can keep your inverter running at peak performance.
- Schedule annual inspections and firmware updates to ensure all components are operating correctly.
- Use weather-rated enclosures (IP65 or higher) to protect outdoor units from rain, dust, and corrosion.
- Optimize string design during installation to avoid mismatch losses from shading or uneven panel orientation.
- Keep ventilation paths clear and clean inverter filters regularly to prevent overheating.
- Avoid oversizing the system far beyond the inverter’s rated capacity.
- Monitor inverter temperature and daily yield using the manufacturer’s app or portal.
Implementing these practices can result in an energy gain of 3–7% annually—especially significant for high-consumption homes and commercial systems with long operating hours.
image: inverter-efficiency-tips.png
This seemingly modest improvement adds up over time, especially when energy costs are high or systems run continuously. A small investment in maintenance can lead to thousands in long-term energy savings.
FAQ About Solar Inverters
Q1: Which solar inverter is best for home use?
Micro inverters or hybrid inverters depending on roof layout and battery needs.
Q2: Do solar inverters work without batteries?
Yes. Grid-tied and string inverters work without batteries. Only hybrid/off-grid inverters use storage.
Q3: How long do solar inverters last?
Typically 10–15 years. Premium models may last over 20 years with maintenance.
Q4: Is remote monitoring important?
Yes. It helps detect faults early and reduce downtime, especially in large systems.
Q5: Can I install inverters outdoors?
Yes, if the model has a high ingress protection rating (IP65 or above).
Conclusion & Next Steps
Choosing the right solar inverter means maximizing your energy production, ensuring safety, and reducing long-term costs. Whether you’re powering your home, building a rooftop array for your business, or managing a utility-scale project, the inverter you choose in 2025 will define your system’s performance.
With growing demand for solar energy in residential and commercial markets, future-ready inverter solutions with smart features and robust support will be the key to success for installers, homeowners, and B2B buyers.
Ready to Source the Right Solar Inverter?
🔧 Request a Quote for Bulk Orders or OEM Service
Written by Howard, Senior Technical Consultant at Guangzhou Eco Echo Power Co., Ltd., with over 5 years of experience in solar power system design and international B2B and residential project support.